Introduction to Java

Instructor: Chris Fulton
Learning Objectives
- Explain the necessary components needed to download, run and execute a Java program
- Context - Java | Java API | Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
- What is needed - Editors, Compilers, and Interpreters
- Interpret a basic Java program
- Project structure | import | Main() | Method Declaration | Method Body | Statements
- Explore the declaration and use of variables
- Java primitive data types
- Variable declaration and initialization | Parsing and Casting
- Execute, compile and debug a basic program
- Types of Errors: Compile-time | Run-time | Logical
- Debugging and Commenting Code
- Utilizing Java API - Java System Class
- Creating Interactive programs using Scanner Class| Escape Sequences | Formatting
- Utilizing source control to keep track of changes, track history and experiment with code
- Downloading starter code and uploading Programs using Git
- Overview of Version Control using Git
Context
Java
is an object oriented programming language
Java is accompanied with the Java API or standard class library
Developed in early 1990s by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems which is currently owned by Oracle
Standard Class Library
the standard class library or Java API is provided software/code that gives you the ability to create graphics, communicate over networks, and interact with databases, among other features
Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
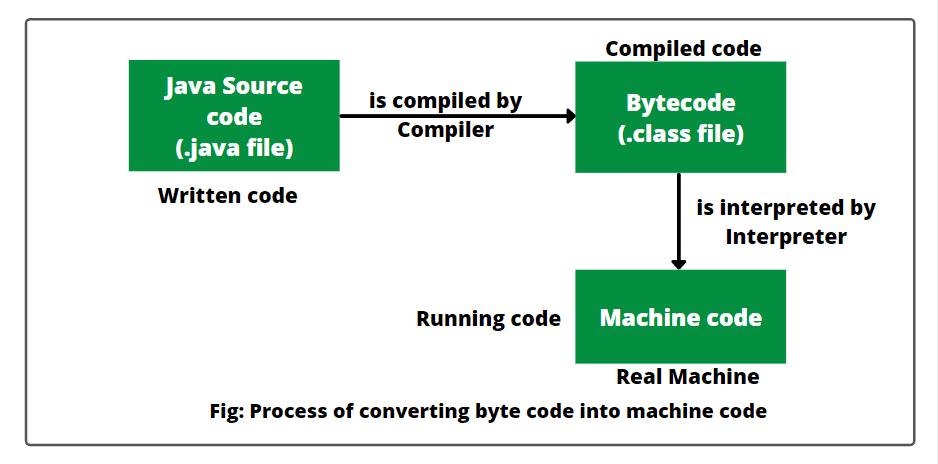
The JVM has two primary functions: to allow Java programs to run on any device or operating system (known as the "Write once, run anywhere" principle), and to manage and optimize program memory.
The JVM makes it possible to translate bytecode into machine code
What is needed to run Java?
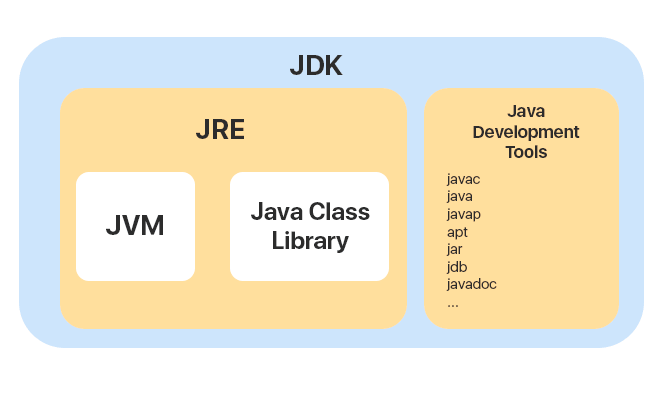
The JDK (Java Development Kit)
Contains two major parts
- The Java Runtime Environment (JRE) includes:
- Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
- Java API or Java Standard Class Library
- Java Development Tools
- Java Compiler aka
javac - Java documentation aka
javadoc - Java Archive Resource files aka
jar - etc...
JDK Overview
Tutorial to install JDK w/VS Code Text Editor
The JVM primary job
Java Terminology and Components - learning activity
Match the command with the description to the right by dragging and dropping term into box.
Sample Program Break-down
Program Components
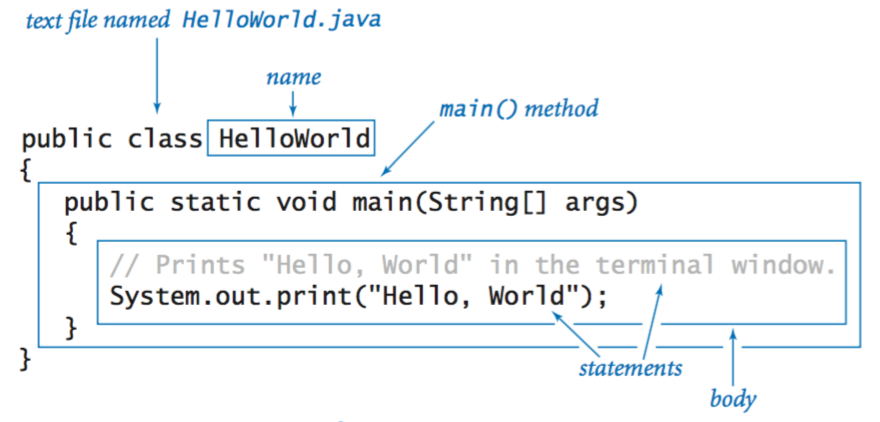
- Java main method
- Method header
- Includes the access modifier - Who can access the method
- Includes what will data type will be returned from method. *In the image above, the method returns void "nothing"
- Includes the method name and information about what will pass into and be returned from a method
- Method body
- Contained within a pair of curly braces and includes all the instructions executed by the method
- Access Modifier
- Defines the circumstances under which the method can be accessed
- default, public, private, protected, etc..
- Keywords
- Predefined and reserved identifiers that have special meaning to the compiler
- The name of the method is
main() - Every program must have a
Main()method - Classes with a Main()method are called application classes; others are non-application classes
- Packages
- To control access; avoid naming conflicts, used to group related classes. Can be thought of as a folder in a file directory
- Two categories of packages
- Built-in Packages (packages from the Java API)
- User-defined Packages (create your own packages)
Declaring & Initializing Variables
Terms
Constant
Cannot be changed after a program is compiled. Utilize keyword "final"
Literal constant
Its value is taken literally at each use
Variable
A named location in computer memory that can hold different values at different points in time
Data Type
Describes the format and size of (amount of memory occupied by) a data item
Primitive Types
types that are self contained and holds atomic value; Types without any fields or methods; Types do not inherit Object. Primitive data types are also called simple types
Unicode
is the system that provides a numeric value for every character.
Data Types
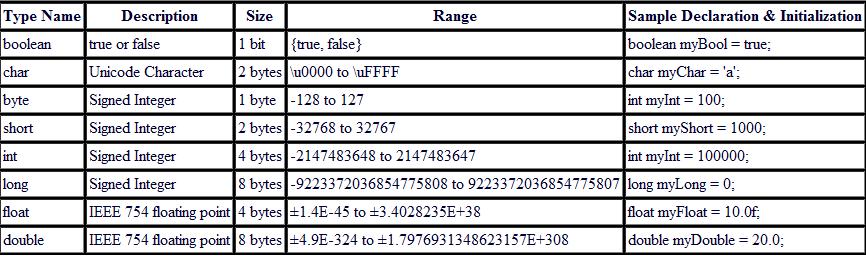
What does it mean by signed and unsigned? What's the difference between bit and bytes?
Learning Activity - number guess boxes
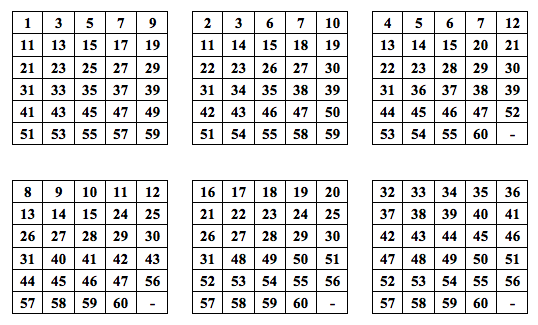
Think of a number between 1 - 60
Do not share this number with the instructor. The instructor will magically guess your number
How did I guess the number?
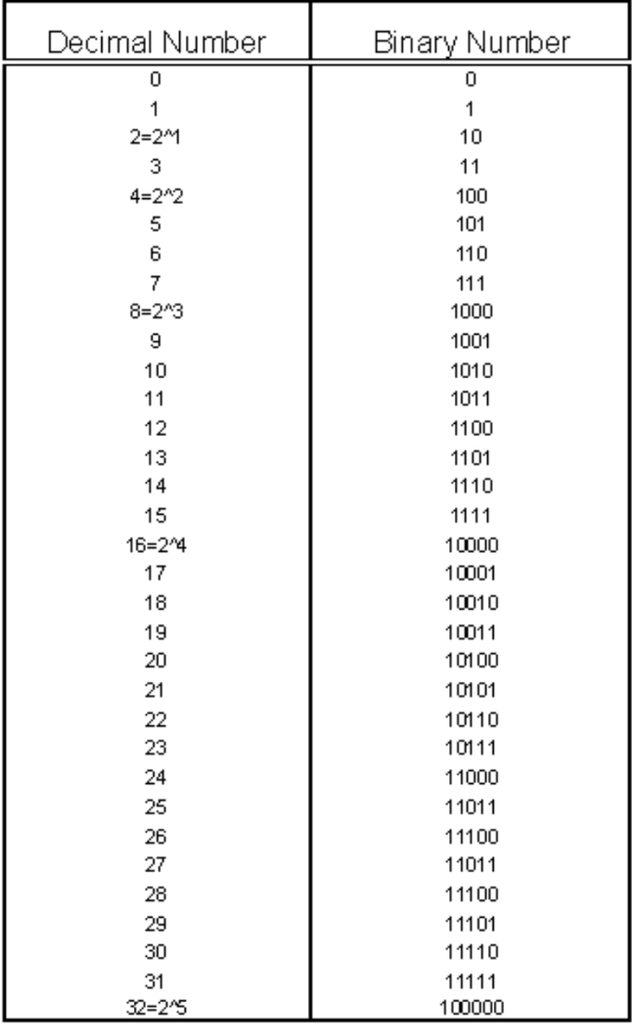
Unicode - ASCII - Binary
Learning Activity - Binary
Patterns?
Are there any recognizable patterns you observe from the chart to the right?
Decimal to Binary
Convert the number 92 and 203 into Binary
Binary to Decimal
What is the decimal value of 10010110?
What is the decimal value of 0110101?
Reserved var keyword
class Program
{
static void aMethod()
{
//Using primitive data type
double monthlySalary = 9200.00;
//Using Var keyword
var yearlySalary = monthlySalary *12;
System.out.println(yearlySalary);
}
}
Java lets you declare local variables without giving them explicit types. The data type is implied at runtime.
Compiling, Debugging and Executing a program
Possible Errors in Execute, Compile and Debug a Java Progam
Syntax Errors
Logical Errors
Run-time Errors
When compiling and running a program, any of the three errors can occur.
Steps to compile via command line
Step 1
Open the terminal
Step 2
Make sure you in the directory you want to compile source code
Step 3
Enter the commandjavac [NAME_OF_FILE].java to compile
Step 4
type the Dir command to view files (this step is not necessary for compiling)
Step 5
Type java [NAME_OF_FILE] and press Enter to run the program. * Make sure to leave .java off
Syntax Error
- Common Syntax/Compile Time errors: Missing Semicolon; Missing opening and closing bracket; Mis-spelled keyword; Incorrect case (uppercase vs lowercase characters).
Incorrect
public class Movie{
public static void main(String[] args) {
string marvelMovie = "The Avengers Infinity War"
System.out.printLine(marvelMovie + " is the best Marvel Movie");
}
Correct
public class Movie{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String marvelMovie = "The Avengers Infinity War";
System.out.println(marvelMovie + " is the best Marvel Movie");
}
}
Logical Error
- Logical errors (Hardest to Detect):Incorrect calculations; Using incorrect operator; Using wrong variable for output or calculation
Incorrect
public class Discount{
public static void main(String[] args) {
double price = 23.00;
double discount = .10;
price = discount *(price - 1);
System.out.println("With discount the price is " + price);
}
}
Correct
public class Discount{
public static void main(String[] args) {
double price = 23.00;
double discount = .10;
price = (1 - discount) * price;
System.out.println("With discount the price is " + price);
}
}
Run-time Errors
- Run-time Errors: Dividing by zero; Mismatch variable data type assignment; Forgetting to close a file
- Asking the computer to do something that it is unable to do or complete properly
Incorrect
public class Calculations{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number1 = 32, number2 = 0, result = 0;
result = number1/number2;
System.out.println("The result is" +result);
}
}
Correct
public class Calculations{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number1 = 32, number2 = 0, result = 0;
try{
result = number1/number2;
System.out.println("The result is" +result);
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println ("Can't be divided by Zero " + e);
}
}
}
Quiz Question
class Program{
public static void main(String[] args){
//Using primitive data type
double monthlySalary = 9,200.00;
//Using Var keyword
var yearlySalary = monthlySalary *12;
System.out.println(yearlySalary)
}
}
How many errors do you observe in the code above?
Quiz Question
public class Program{
public static void Main(String[] args){
//Annual Salary
double annualSalary = 92003.14;
//Calculate the monthly Salary
double monthlySalary = annualSalary * 12;
System.out.println("Monthly Salary: $" + monthlySalary);
}
}
Using the code above, which option represents the error in the code?
Debugging in Visual Studio Code
- Debugging
- The process of removing all syntax and logical errors from the program
- Syntax errorsare discovered through compilation. Logical errors are discovered through testing
- Commenting out portions of your code is another way to help debug and narrow the issue.
- 1) Set a breakpoint. 2) Open Debug window - play button that has bug on it. 3) Step through code and observe variable assignment and call stack.
System and Scanner Class
Scanner Class
To implement the Scanner class, you must import import java.util.*;package
The Scanner class allows for input operations - reading input from the console
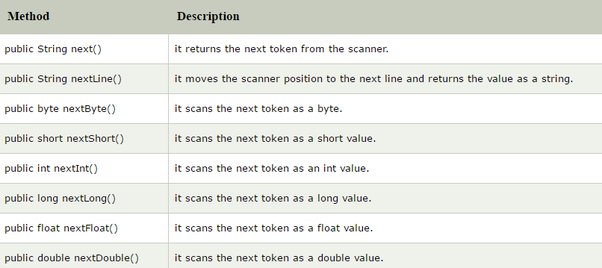
Analyzing Program w/Scanner Class
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Program{
public static void main(String[] args){
//Declarations
String name, program;
int creditHours;
double tuitionCost;
final double TUITION = 780.00;
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in); // Create a Scanner object
System.out.println("Please enter your name: ");
name = scn.nextLine();
System.out.println("Please enter program: ");
program = scn.nextLine();
System.out.println("Please enter number of credits for this semester: ");
creditHours = scn.nextInt();
tuitionCost = TUITION * creditHours;
System.out.println(name + " Thank you for entering your information. \n" +
"Your tuition for the semester is: " + tuitionCost);
}
}
System Class
The System package is imported by default, no need for an import statement
The System class offers access to input/output operations, but can also provide access to system level information.
Analyzing Program w/System Class
import java.util.Scanner;
class Program{
static void Main(String[] args){
long startTime = System.nanoTime(); //Gets the time before evaluating next statements
System.out.println("Your System properties");
System.out.println("**********************");
Properties p = System.getProperties(); //Creating a new instance of
System.out.println("User name: " + p.getProperty("user.name")); //get User's account name
System.out.println("User home directory: " + p.getProperty("user.home")); //get User's home directory
System.out.println("User current working directory: " + p.getProperty("user.dir")); //get User's current working directory
System.out.println("User Operating System: " + p.getProperty("os.name")); //get operating System
System.out.println("User Operating System version: " + p.getProperty("os.version")); //get operating system version
long elapsedTime = System.nanoTime() - startTime; //Calculate after executing getProperty() statements
// 1 second = 1_000_000_000 nano seconds
double elapsedTimeInSecond = (double) elapsedTime / 1_000_000_000;
System.out.println("Time in seconds it took to execute program: " + elapsedTimeInSecond + " seconds");
}
}
Learning Activity
Gaining inspiration from the previous slide, create a program that calculates the time it takes you to type out the teams "White Sox, Cubs, Sky, Bears, Fire, Blackhawks, Bulls " Your program should operate and function similar to the program below.
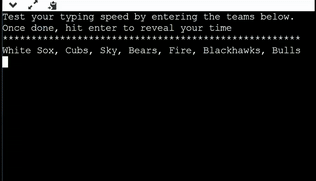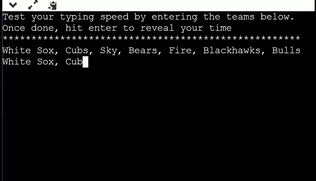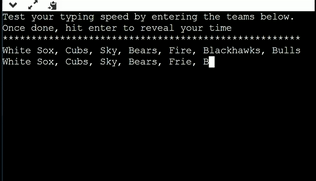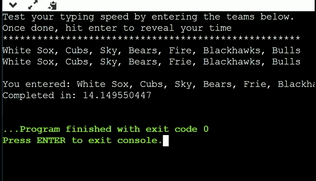
Step 1
Declare variables need for program and create Scanner object instance
Step 2
Create statement to start the timer and display the teams and accept input
*Review previous slide
Step 3
Calculate the starttime from endtime, get time in seconds and display output message
Escape Sequence
Formatting Floating-Point Values
Utilizing Source Control
Version Control + Git
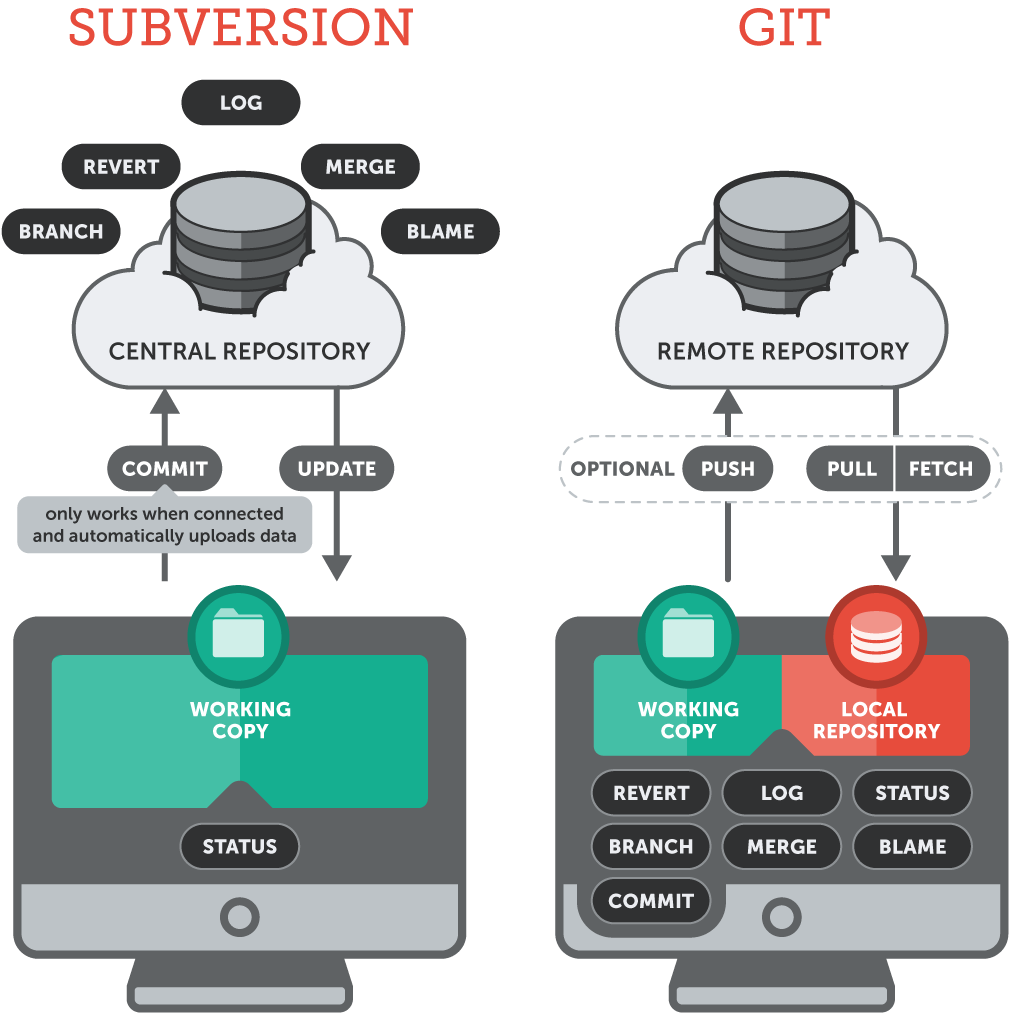
Version Control
The task of keeping a software system consisting of many versions and configurations well organized.
What is Git?
Git is a free and open source distributed version control system designed to handle everything from small to very large projects with speed and efficiency.
Download and install Git
- Navigate to git-scm.com
- Download the latest release for your operating system
- Install using default configurations - For windows a git bash terminal will come with your download. For macs you will use terminal for your git.
- Once downloaded, open the "Git bash" terminal and enter the command
git --version
Installation Configuration
Commonly Used Git commands - Cheatsheet
The cheatsheet represents some of the most used commands that allow you to achieve the Git workflow.
Click here for an exhaustive book on git commands
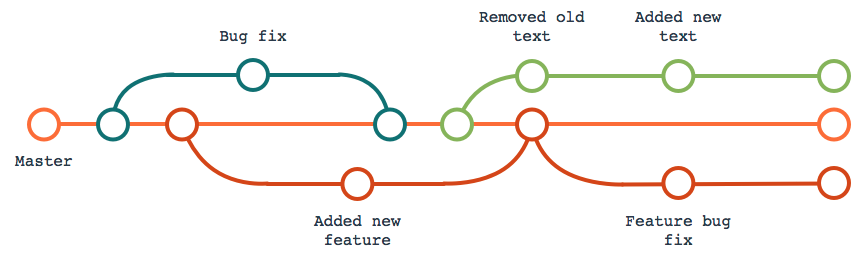
Git workflow
Going through this workflow allows us to keep track of the changes we are making.
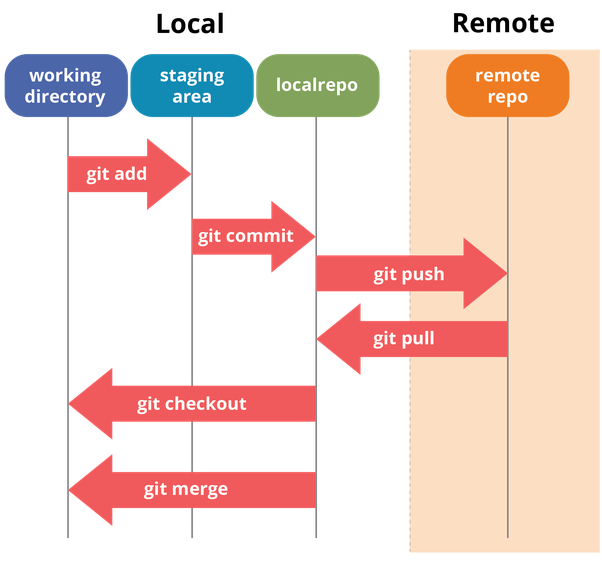
Git Command Practice
public class App{
public static void main(String[] args) {
double price = 23.00;
double discount = .10;
price = (1 - discount) * price;
System.out.println("With discount the price is " + price);
}
}
For this activity, we'll keep track of the changes we make to a simple java program
Step 1
Create a new Java program and copy the code above into your source code -> Open the folder and right-click to open git bash terminal-> initialize git inside of project folder and make first commit.
Step 2
Create a public repository on GitHub.com and copy instructions to push existing code to repository
Step 3
Run the git status command and make sure your directory does not have untracked files and to make sure branch is clean.
Navigate back to the the terminal and paste commands to push code up.
Git Workflow and Practice
1. git init -> Initializes git into project folder
2. Make the necessary changes to the application. Save the file and render in browser to observe added functionality.
3. git status -> Checks the status to see status of files in directory
4. git add . -> Adds files to staging area. In preparation to be committed.
5. git status -> Check status again to see if file(s) were added to staging area.
6. git commit -m "adding category" -> Document the change by committing changes and adding a brief message.
7. git log -> To view commit history and timestamp.
Get Commands - Check for understanding
Match the command with the description to the right by dragging and dropping term into box.
Git Branching & Merging
Branching allows you to create a copy of your main branch. You can experiment and test new functionality on new branches. Branching allows you to keep your main branch clean.