Introduction to User Experience

Instructor: Chris Fulton
Learning Objectives
- Contrast the difference between user interface (UI) and user experience (UX)
- UX vs. UI
- UX components
- Analyze various User Research methods used in UX
- Observations | Interviews | Task Analysis | Focus Groups | Surveys | Web Analytics
- Examine best practices used for developing information architecture and navigation
- Identifying Various Content Strategies
- Tools and Techniques - Card Sorting | Use Cases,User Stories, User Personas
- Review Usability tools and testing resources
- Usability Testing | A/B testing | Site Peformance testing: tools, server/hosting | CDN
- Compatibility Testing - Visual Factors | Browsers | device | print
- Review and access accessibility standards
- Standards - WCAG | ISO 9660 | Section 508 | Aria Roles
- Create Wireframes and Prototypes
- Low-Fidelity | High-Fidelity | Tools
What is User Experience(UX)?
User experience focuses on having a deep understanding of users, what they need, what they value, their abilities, and also their limitations. UX best practices promote improving the quality of the user’s interaction with and perceptions of your product and any related services.
UX vs. UI
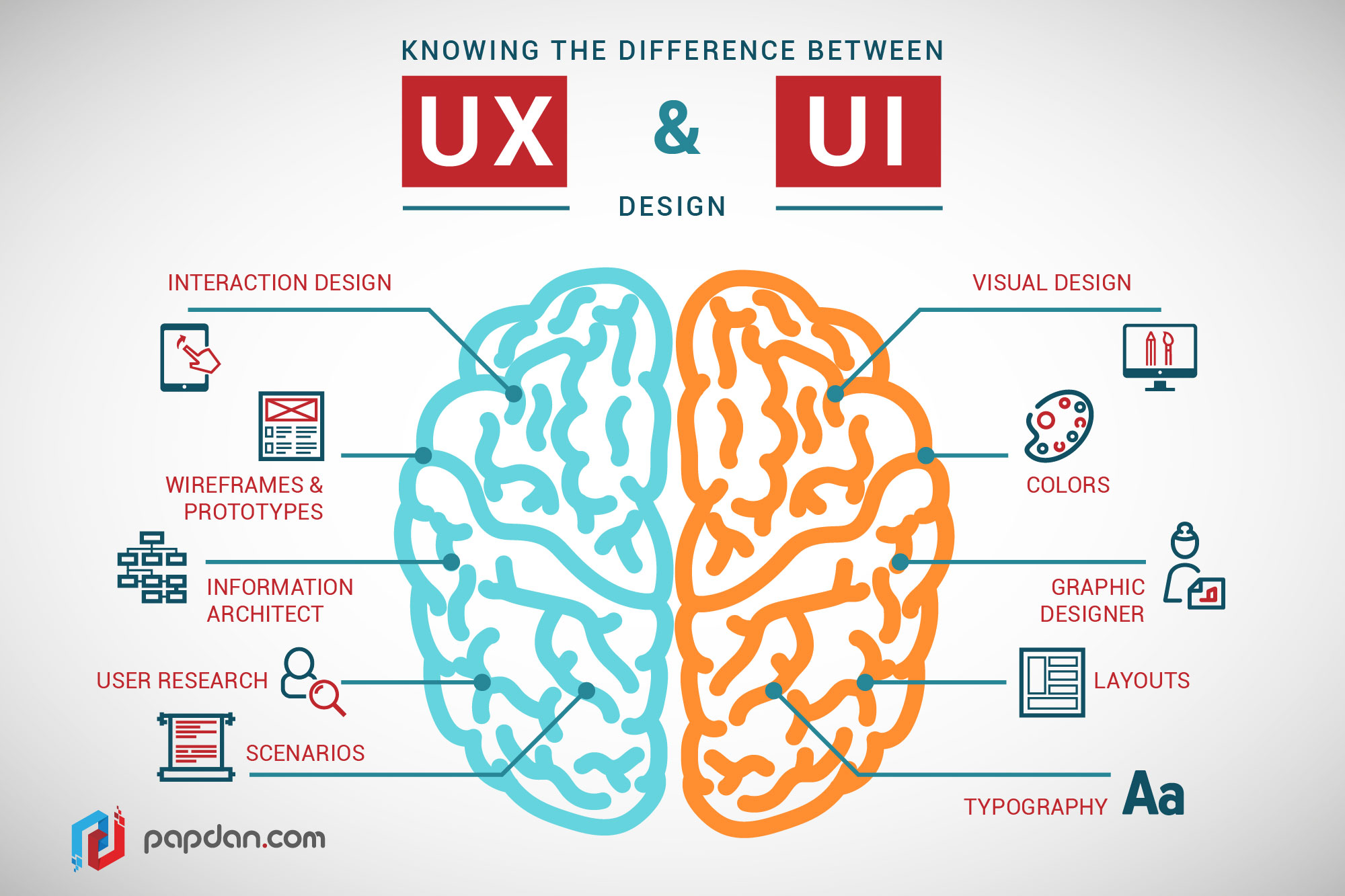
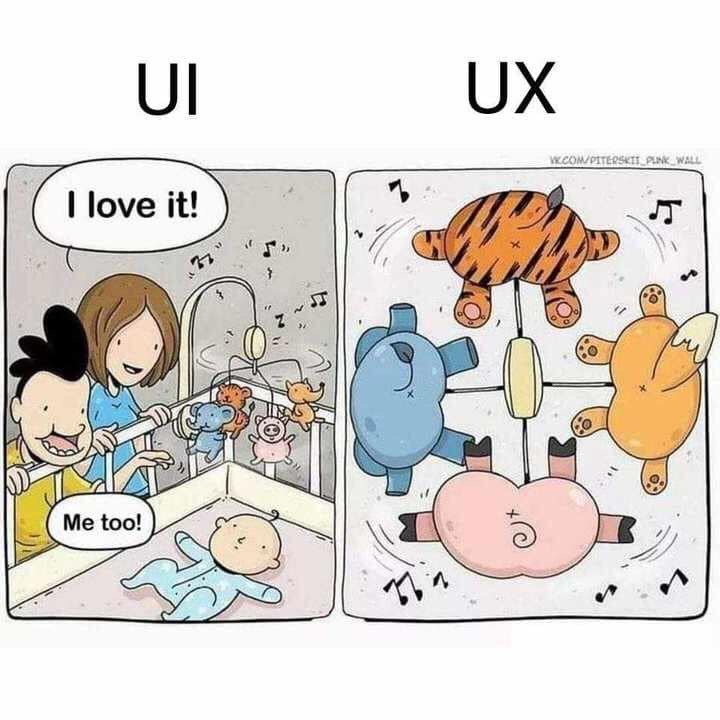
The Echo Silver
User experience is more than data collection. It's about understanding the motivation behind user needs and striking a strategic balance between expectations and business needs.
UX Honeycomb Facets
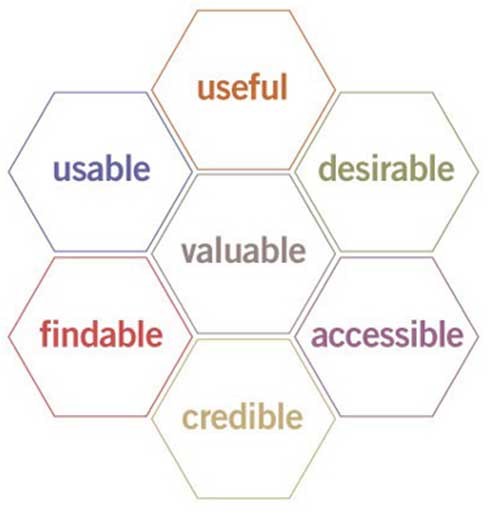
Peter Morville’s UX Honeycomb article
UX Desired Outcome
Useful
Your content should be original and fulfill a need
Usable
Easy to use, Easy to Manuever and understand
Desirable
Image, identity, brand, and other design elements are used to evoke emotion and appreciation
Findable
Content needs to be navigable and locatable onsite and offsite
Accessible
Content needs to be accessible to people with disabilities
Credible
Users must trust and believe what you tell them
Valuable
Feel that they have gained something, moves closer to mission
Lab/Activity
- Conduct research on User experience job descriptions and find common commonalities between the descriptions
- Make a list of of requirements, skills and tools listed for the job descriptions you researched.
Job board sites: Dice.com, indeed.com, simplyhired.com, etc.
Why User Research?
Why User research?
User Research
Observations
Give people tasks or instructions and watch them use your design, without help.
Interviews
Ask prospective users questions about their expectations of your design.
Task Analysis
learning about user goals, and understand the tasks users will perform on your site.
Focus Groups
a moderated discussion where you can learn about users’ attitudes, beliefs, desires, and reactions to concepts.
Surveys
a structured questionnaire that your target audience completes over the internet generally through a filling out a form
Nielsen Norman Group Research
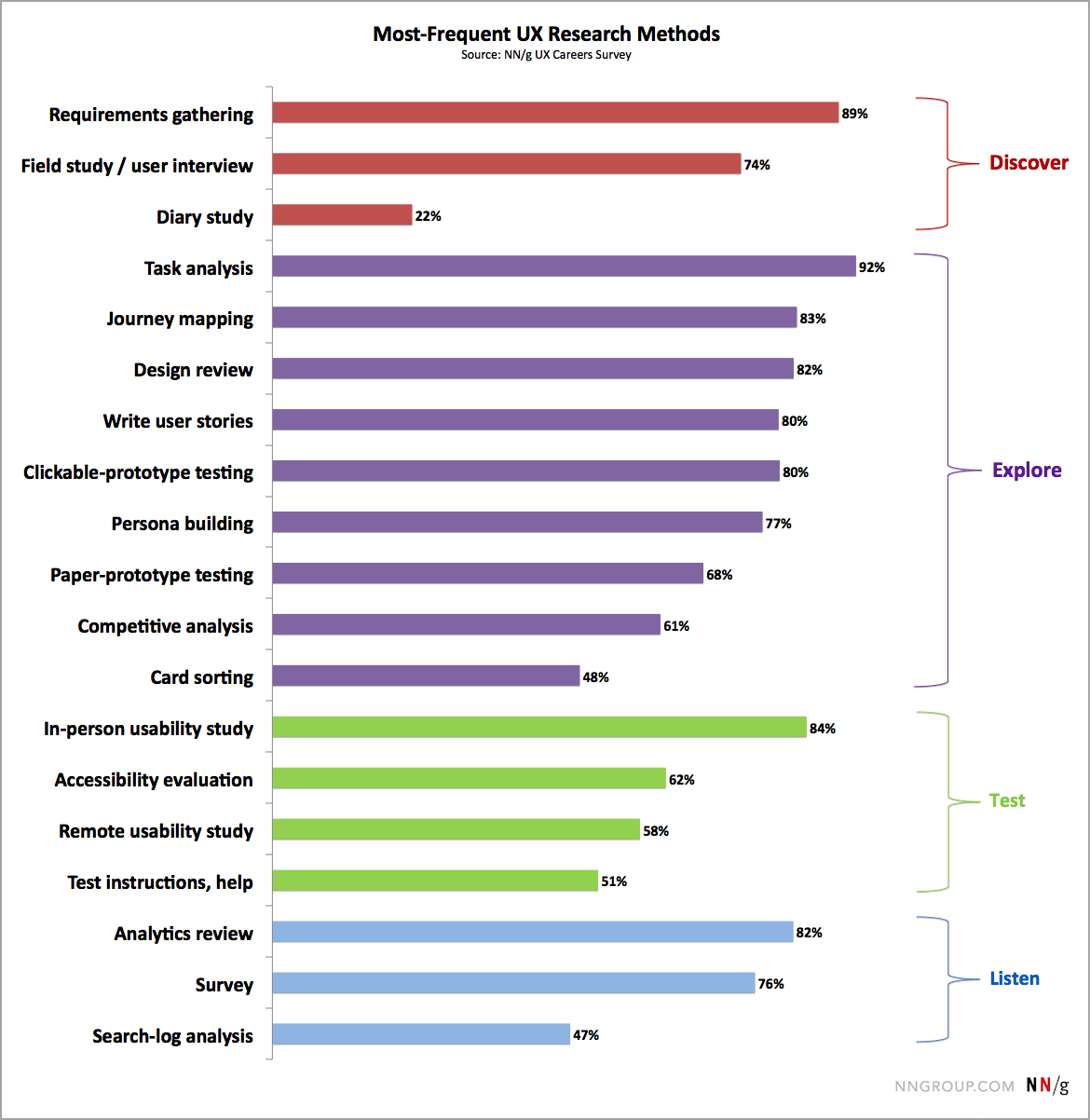
NN UX Activities
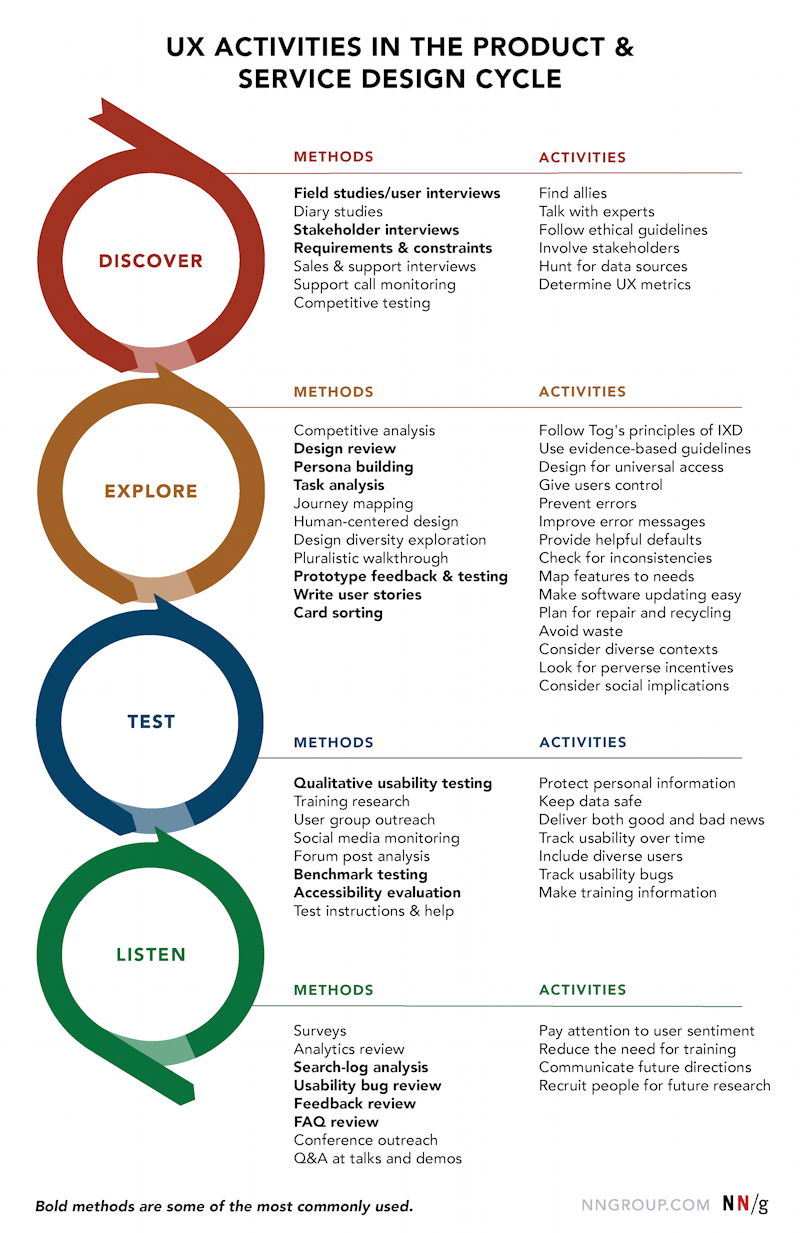
When to use which UX research method
UX Quadrants
UX research can be categorized into four quadrants
Helpful in identify what to measure and what type of feedback/data the team is looking to capture
| Class | Description |
| Attitudinal | Focuses on what people say versus what they do |
| Behavioral | Focuses on what people do versus what they say |
| Qualitative | Focuses on the why and how |
| Quantitative | Focuses on How much and how many |
UX Design Process
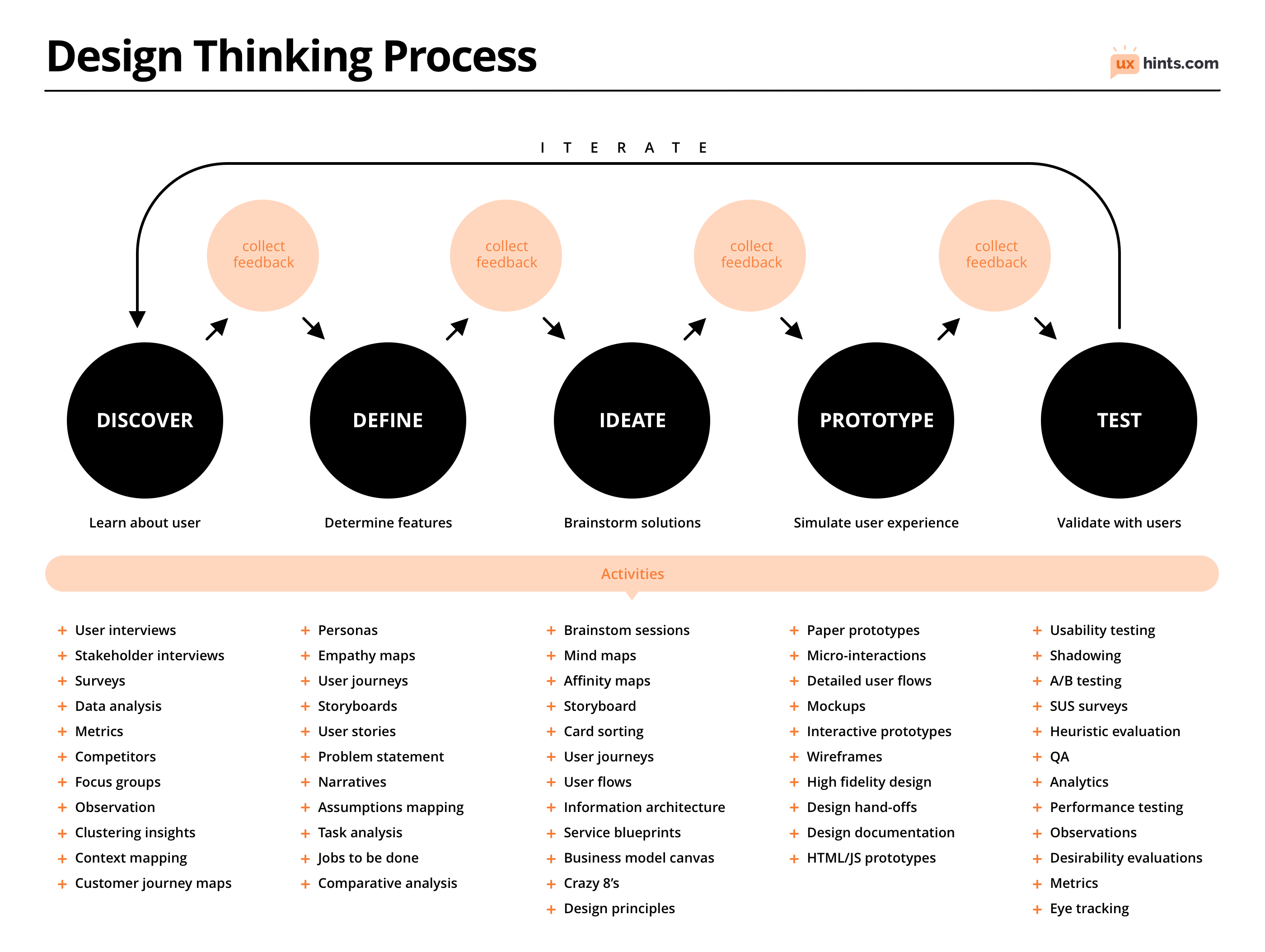
User Personas in Scope
What is the Goal of User Persona's?
User Personas
DO
- Base persona on research
- Gather data from anayltics
- Make realistic, personable and goal oriented
- Create as a team
- Focus on the present
- Give persona image and name
- Get buy-in from all involved
DON'T
- Generate based on assumption
- Create in a silo
- Over generalize characteristics
- Create personas that focus on ideal or perfect customer
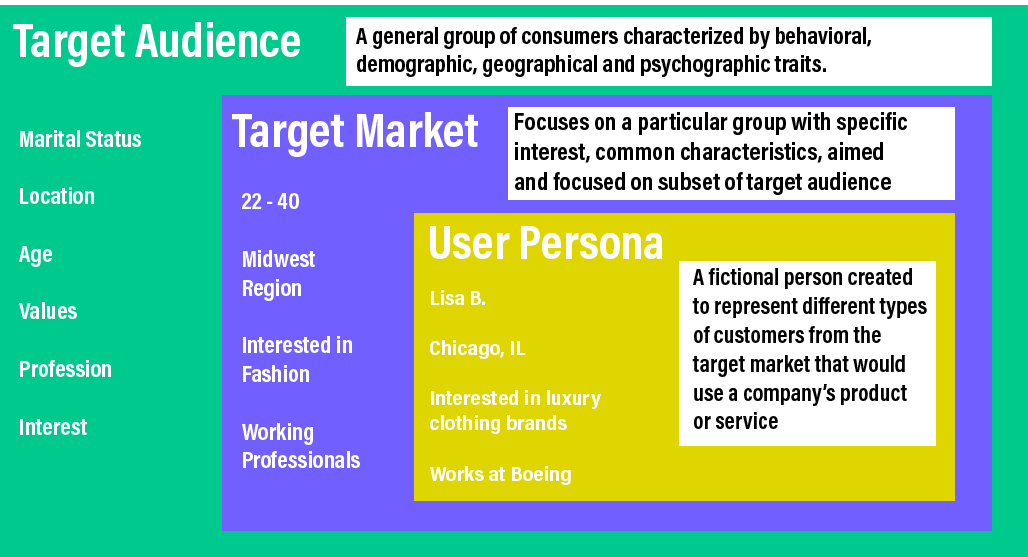
User Personas example
Information Architecture (IA)
Understanding Navigation
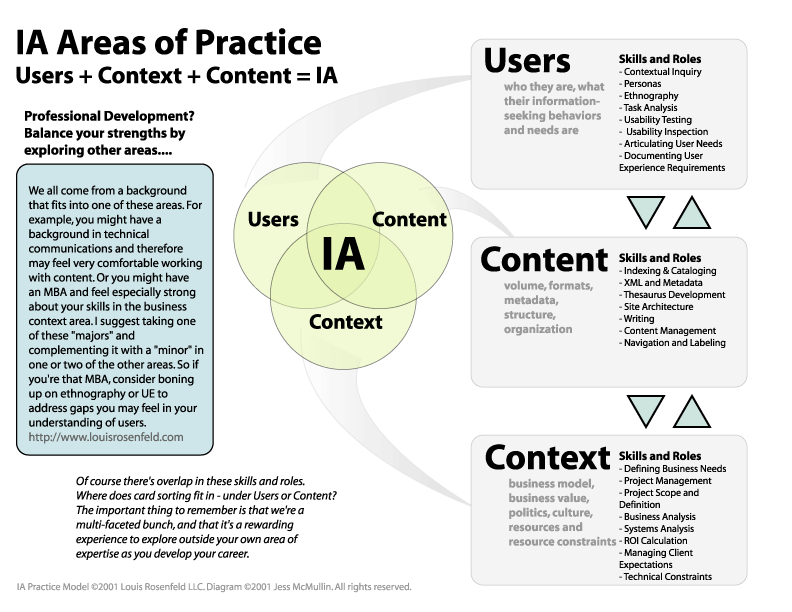
Information Architecture and navigation considerations
- Information design is the most important factor in the success of your site
- What do users want when they get to your site?
- Anticipate and plan for user actions
- Do not make users navigate through too many layers of information
- Follow the three clicks rule
- Use consistent navigation
- Provide direct links to your most popular pages
Navigation Considerations - Orient the User
Provide enough location information to let the user answer the following navigation questions:
- Where am I?
- Where can I go?
- How did I get there?
- How do I get back to where I started?
Card Sorting Activity

- While observing the picture above, write down as many items and characteristics you can find. Please adhere to the rules below
- Using index cards or post its - write down one item per card/post it.
Understanding Card Sorting
Sample Website Architecture
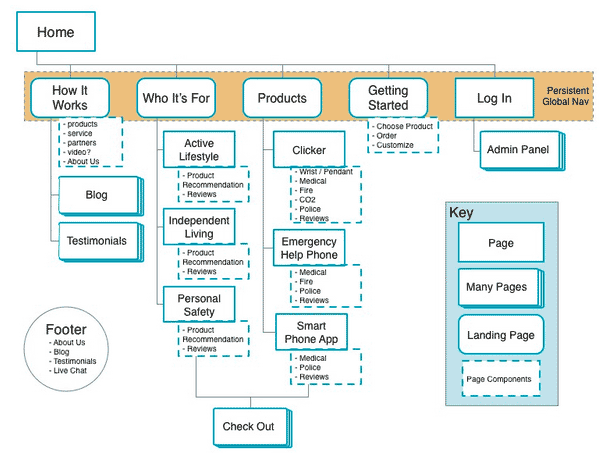
Sitemap Activity
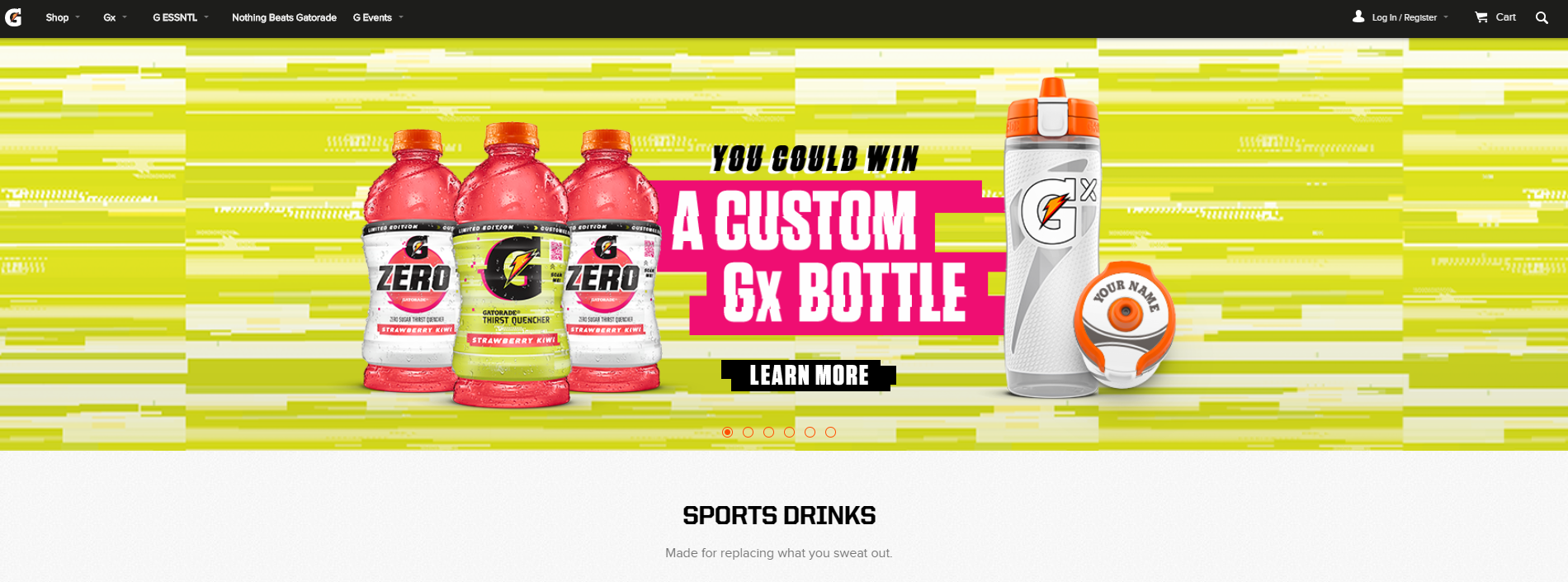
- Navigate to Gatorade.com and construct a sitemap based on the site's content using Draw.io. Make sure to include the following within your sitemap.
- The site-maps key/legend that describes each shape represented in your sitemap. Your key/legend should have a minimum of 3 different shapes.
- The persistent global navigation which defines the page names and order of pages.
- The page components or sub-pages that stem from your global navigation.
- The static footer content that will be persistent on each page.
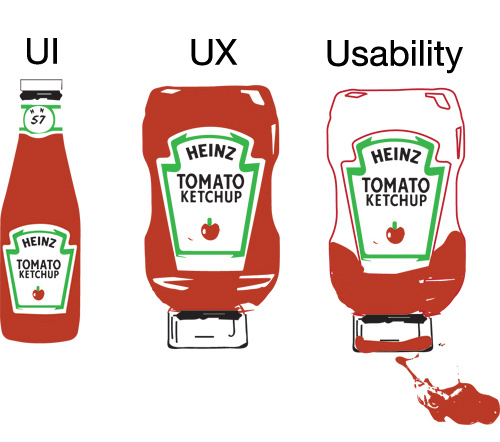
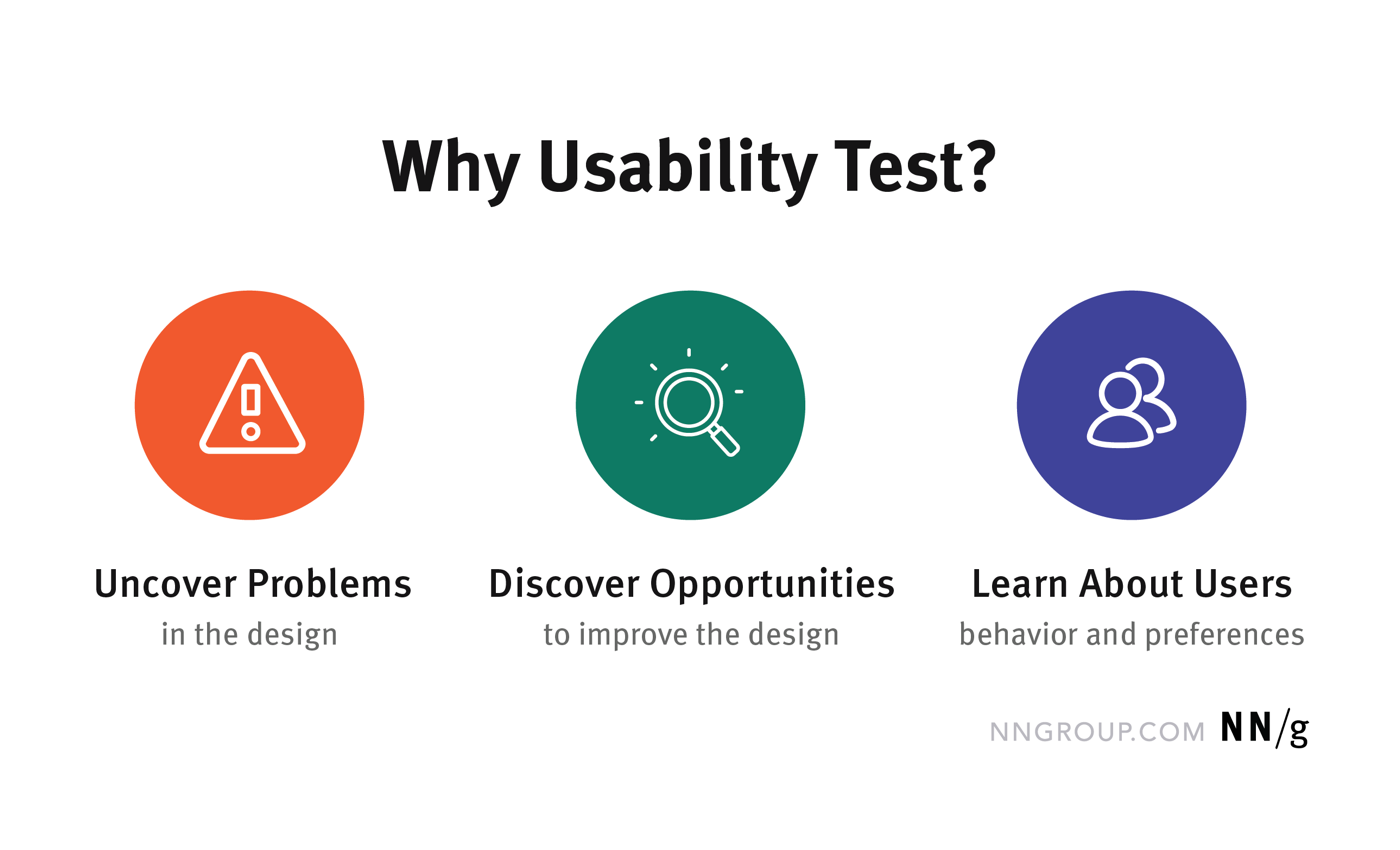
Why Usability?
Why Usability Testing
10 Usability Heuristics
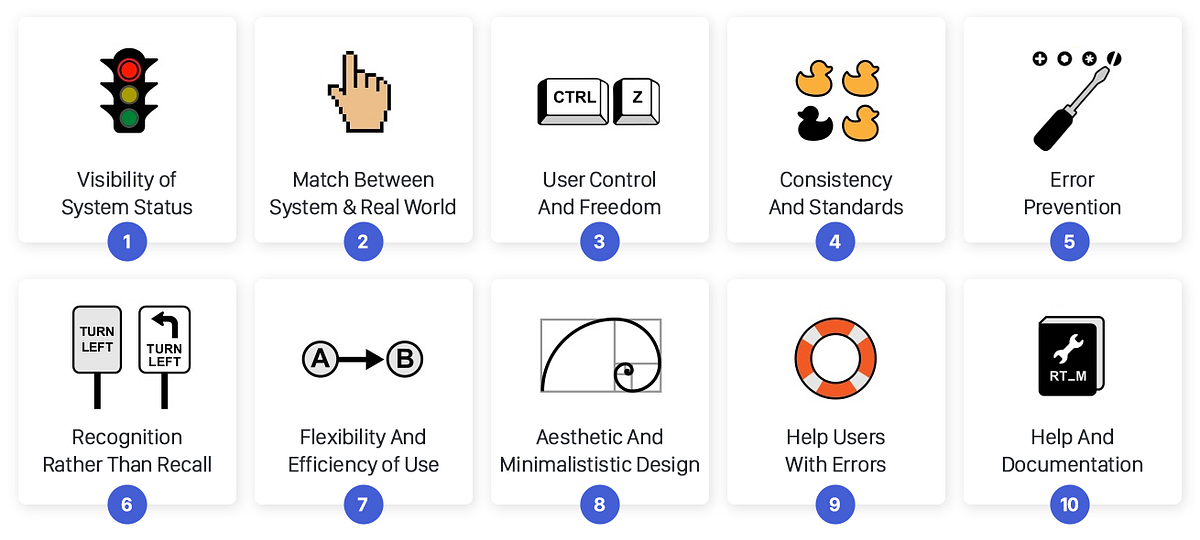
Usability Components

Usability refers to the ease of access and/or use of a product or website.
Website Usability
Website usability considerations
- Speed, Uptime
- Site errors - broken links
- Visual Factors
- Color Choice
- Presentation of Content - https://www.webpagefx.com
- Accessibility related maters
- Browser and device compatibility
Accessibility
Introduction to Web Accessibility
Accessibility Principles
Perceivable
People can see the content or hear it
Operable
people can typing or by voice
Understandable information
people get clear and simple language
Robust content
people can use different assistive technology
Accessibility Tools and Resources
WAVE Web Accessibility Evaluation Tool
WAVE can identify many accessibility and Web Content Accessibility Guideline (WCAG) errors, but also facilitates human evaluation of web content.
The A11yProject
A checklist that uses the the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). You can access the list here
Web Accessibility Evaluation Tools List
Web accessibility evaluation tools are software programs or online services that help you determine if web content meets accessibility guidelines.
Learning Activity

Step 1
Identify a website that utilizes color and identify a 1 page of the site to evaluate.
Step 2
Perform a color evaluation on the site using the link below and observe areas of the site that meet the ratio standard and areas of the site that fall short of the standard.
https://color.a11y.com/?wc3
Step 3
Using the color picker in the browser developer tools, make a recommendation of closely related colors that would pass meet the minimum ratio level.
Wireframing and Prototyping
Prototypes vs Wireframes
A wireframe is a two-dimensional illustration of a page’s interface that specifically focuses on space allocation and prioritization of content, functionalities available, and intended behaviors.
Benefits of wireframing
Visualizing
Visualize structure and formation of how content will be presented.
Error Prevention
allows you to catch mistakes and issues that can occur
Experimenation
allows for trying out more than one layout design.
Prioritizing
determination of how much space to allocate to a given item and where that item is located.
IA Clarity
consistent ways for displaying particular types of information on the user interface
Wireframing Process
Many processes you can take

Wireframing
Low Fidelity ✦ High Fidelity
- Low Fidelity - help facilitate project team communication and are relatively quick to develop. They tend to be more abstract because they often use simple images to allocate space and implement mock content, or Latin (lorem ipsum) text as filler for content and labels.
- High Fidelity - are better for documentation because of their increased level of detail. These wireframes often include information about each particular item on the page, including dimensions, behavior, and/ or actions related to any interactive element.
Low Fidelity Example
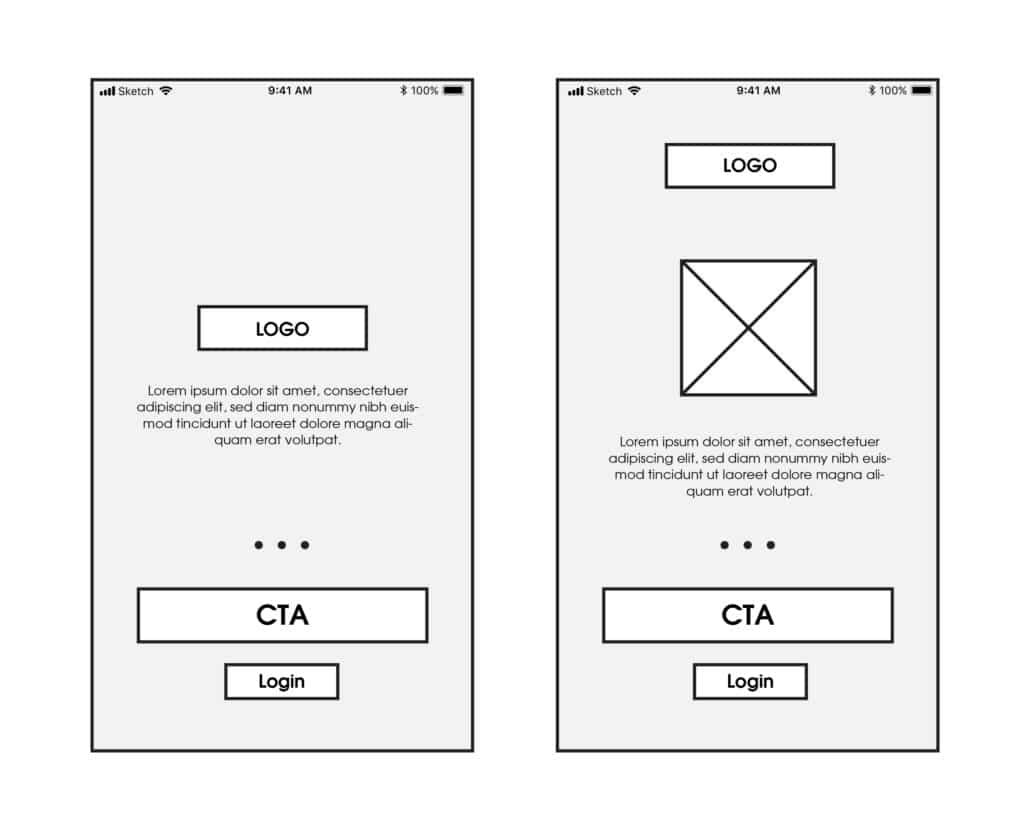
Can be a sketch, general outline of box elements (header, logo, footer, columns, navigation), descriptive text. Black, gray and white used for content and placeholder graphic to allocate space is typically used.
High Fidelity Example
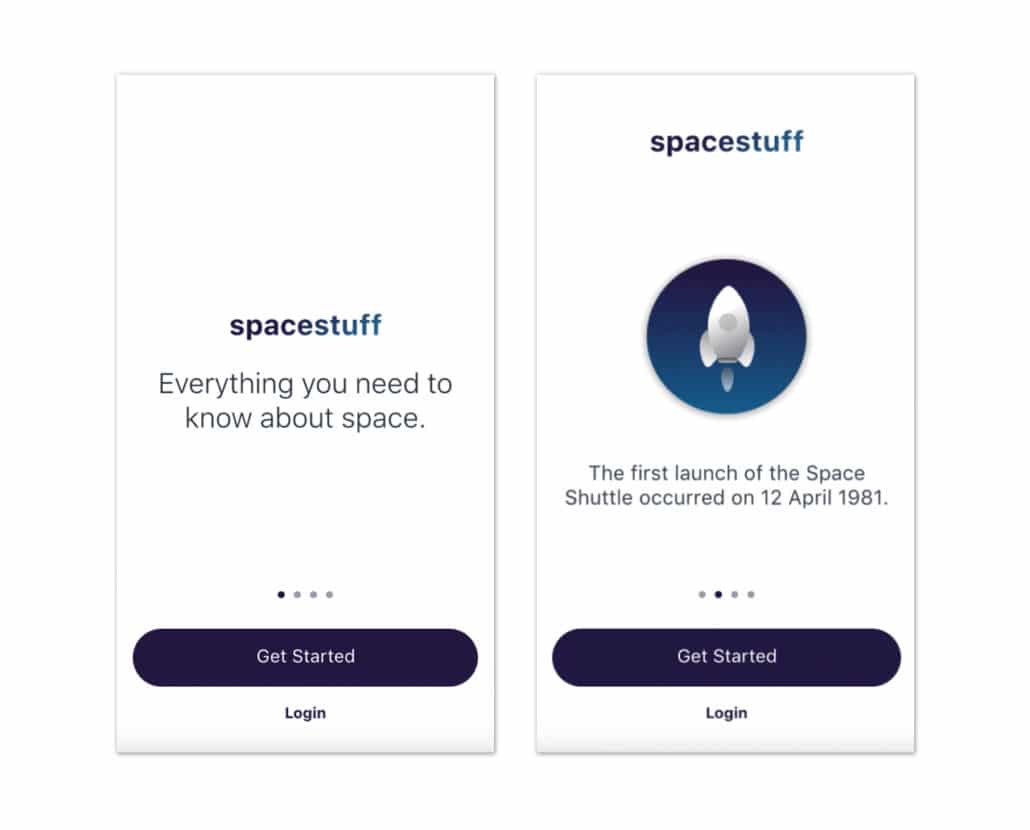
Detailed, precise measurement, every box element is outlined. Graphics, images and color scheme included.
Wireframing Tools
Wireframing/Prototyping using Adobe XD
UX Lab
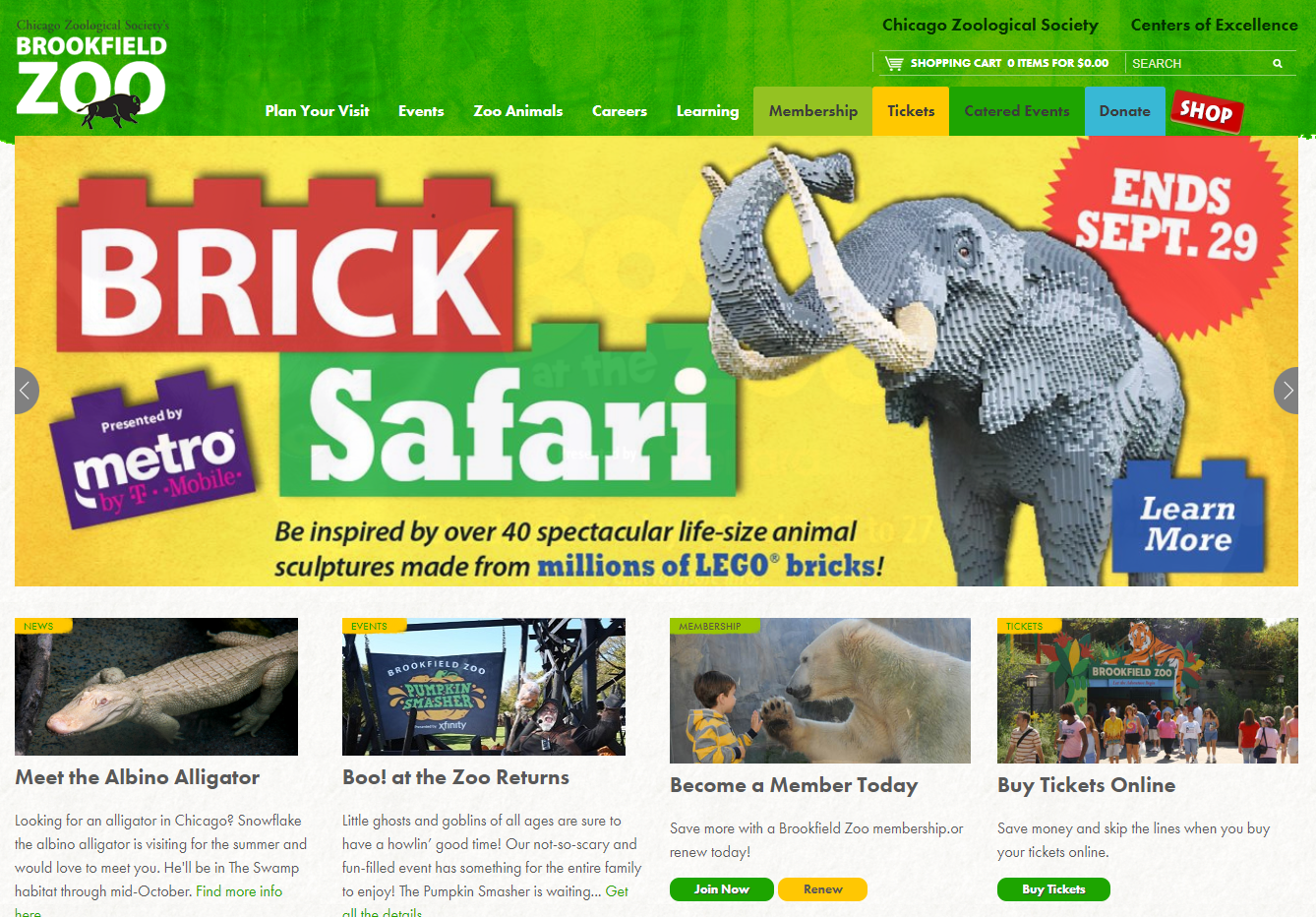
- Navigate to the Brookfield Zoo website and complete the following steps
- Create a high-fidelity wireframe of Brookfield Zoo homepage using Adobe XD
- Provide 2 specific recommendations for improving the site performance as it relates to how fast the homepage renders in the browser
- Provide 2 specific recommendations for improving the accessibility of the site.
Video Lectures
References
- https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/topics/ux-design
- https://webdesign.tutsplus.com/articles/a-beginners-guide-to-wireframing--webdesign-7399
- https://studio571.com/portfolio-items/wireframes-and-prototyping/
- https://mentormate.com/blog/low-fidelity-wireframes-vs-high-fidelity-wireframes/