Http Headers + CORS + REST/RESTFul API
Understanding Headers and making request/response

Objectives
- REST/RESTFul API
- Example using Chucknorris.io API
- Tools
- NPM Packages
- Http Headers
- CORS
- Message body Information
- Security
REST/RESTFul API
What is the difference?
REST/RESTFul API
REST(Representational State of Transfer) Partner with someone and think about important factors you need to consider when implementing Authentication. Consider the two buckets below.
REST
Architectural Constraints or set of Guidelines
- Sessions not used and should be Stateless. *No information stored
- Uses HTTP protocol *Use of GET,POST, PUT, DELETE
-Access resources using URL and returns JSON, XML.
RESTFul
A service that implements the Constraints and Guidelines
Conforming to theses guidelines affords faster, lightweight, and increased scalablity
Video Explanation of REST
REST API TOOLS
REST Tools
HoppScotch - Easy to use web-based interface
Postman - Browser extension, Desktop application
Curl - Quick testing commandline interface
Insomnia REST - Commercial SaaS product and Limited Free version
Example using Curl
curl https://api.chucknorris.io/jokes/random //Simple GET request curl -d "id=1&createdAt=2021-02-27T08:57:20.804Z&name=Chris&avatar=null" -X POST https://603a806df1d6aa0017a10c48.mockapi.io/users
Node Modules and NPM Packages
http/https node.js core modules - A good resource can be found here
npm package axios - Good documentation new website at https://axios-http.com/
Example using axios
const axios = require('axios'); //npm install axios // Make a request for a user with a given ID axios.get('/user?ID=12345') .then(function (response) { // handle success console.log(response); }) .catch(function (error) { // handle error console.log(error); }) .then(function () { // always executed });
Http Headers
What is the difference? How does this show up in a web app?
HTTP Header Categories
Authentication
Caching
Request/Response context
Connection Management
Content Negotiation
Message body information
Cookies
Proxies
Security
CORS
Client Hints(Device and Network)
Conditionals
Setting HTTP Headers
// Node.js program to demonstrate the
// response.setHeaders() Method
// Importing http module
var http = require('http');
// Setting up PORT
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3000;
// Creating http Server
var httpServer = http.createServer(
function(request, response) {
// Setting up Headers
response.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html');
response.setHeader('Set-Cookie', ['type=ninja',
'language=javascript']);
// Checking and printing the headers
console.log("When Header is set a string:",
response.getHeader('Content-Type'));
console.log("When Header is set an Array:",
response.getHeader('Set-Cookie'));
// Getting the set Headers
const headers = response.getHeaders();
// Printing those headers
console.log(headers);
// Prints Output on the browser in response
response.writeHead(200,
{ 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' });
response.end('ok');
});
// Listening to http Server
httpServer.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log("Server is running at port 3000...");
});
Or you can use third-party npm packages that will help with configuration such as helmet.js
Security Headers
Headers to consider for security purposes
HSTS
Expect-CT
X-Frame-Options
Content-Security-Policy
CORS
Referrer-Policy
HSTS
- Strict-Transport-Security - This tells the browser to prefer HTTPS over HTTP. The maxAge parameter lets the number of seconds browsers should remember to prefer HTTPS. By default, this figure is 15552000 — or 180 days. You can also include subdomains as well via includeSubDomains
Why do you think this would be necessary? What does this header help mitigate as it relates to security?- hstspreload.org - You can tell browsers in advance that your site uses HSTS, so that first interaction enforces secure channel.
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=expire-time
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=expire-time; includeSubDomains
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=expire-time; preload
//Example
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains
Expect-CT
- Expect-CT - Informs the browser that it should make additional background checks
Why do you think this would be necessary? What does this header help mitigate as it relates to security?- certificate.transparency.dev - Goal is to detect mis-issued or malicious certificates, with earlier, faster than any other method.
Expect-CT: max-age=360000, enforce, report-uri="https://s_reports.mplsrenters.com/report"
X-Frame-Option
- X-Frame-Option - response header can be used to indicate whether or not a browser should be allowed to render a page in a frame, iframe, embed or object
Why do you think this would be necessary? What does this header help mitigate as it relates to security?- Docker course slides example - Site that takes the full range of window using iframe
X-Frame-Options: DENY //page cannot be displayed in a frame, regardless of the site attempting to do so
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN //page can only be displayed in a frame on the same origin as the page itself
CORS
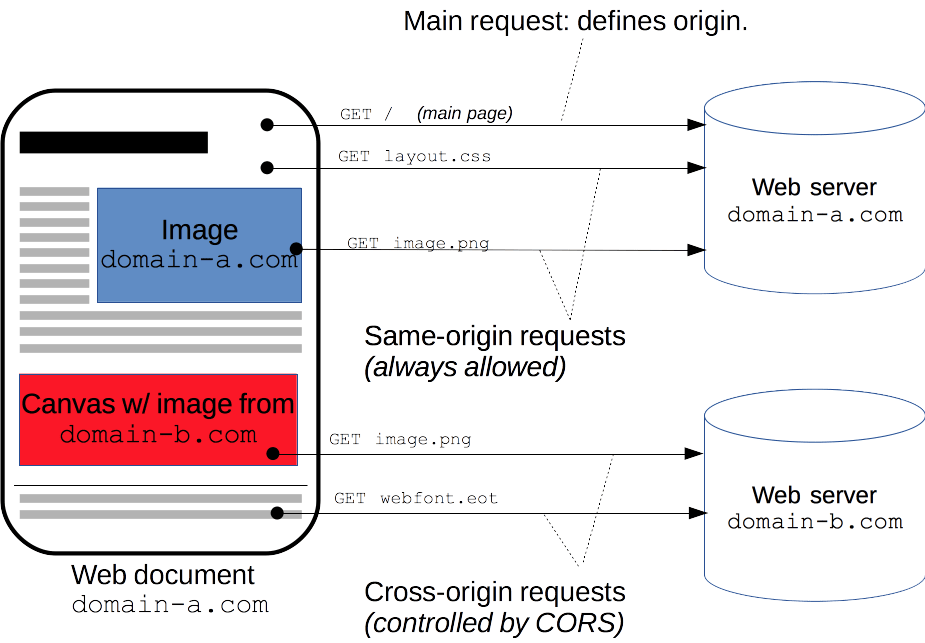
- Cross-origin Resource Sharing - HTTP-header based mechanism that allows a server to indicate any origins (domain, scheme, or port) other than its own from which a browser should permit loading resources
- CORS Preflight - The request is made, but resource prevented. Potentially dangerous due to the abilityt to send data to server.
Referrer-Policy
//Via server
Referrer-Policy: no-referrer
Referrer-Policy: no-referrer-when-downgrade
Referrer-Policy: origin
Referrer-Policy: origin-when-cross-origin
Referrer-Policy: same-origin
Referrer-Policy: strict-origin
Referrer-Policy: strict-origin-when-cross-origin
Referrer-Policy: unsafe-url
//Can also be sent via HTML using the meta tag
- HTTP header controls how much referrer information (sent with the Referer header) should be included with requests.
Question 1
This Http header has parameters that can restrict protocol access and refuse interaction with insecure protocols
- A. Expect-CT
- B. HSTS (Strict-Transport-Security)
- C. Referrer-Policy
- D. CORS
- E. None of the options presented
Question 2
(T/F) HSTS is a trust on first use mechanism? You must visit the site first so that the browser knows that subsequent interaction must use HTTPS.
- A. True
- B. False
Question 3
This Http Header provides an efficient way of monitoring and auditing SSL certificates in nearly real time ?
- A. Referrer Policy
- B. HSTS
- C. X-Frame-Options
- E. Expect-CT
Question 4
Which of the Http headers below helps with preventing clickjacking?
- A. X-Frame-Option
- B. Feature Policy
- C. Referrer Policy
- E. None of the options presented
Question 5
Which of the following can a referrer policy not restrict?
- A. The page from which the end-user navigated from
- B. It can restrict to the origin of the domain
- C. It can restrict to a secure protocol of the origin
- E. None of the options presented. The referrer policy can be set for all of the options presented.